Table of Contents:
-
Market Moving Headlines
-
Interest Rates
-
Currencies
-
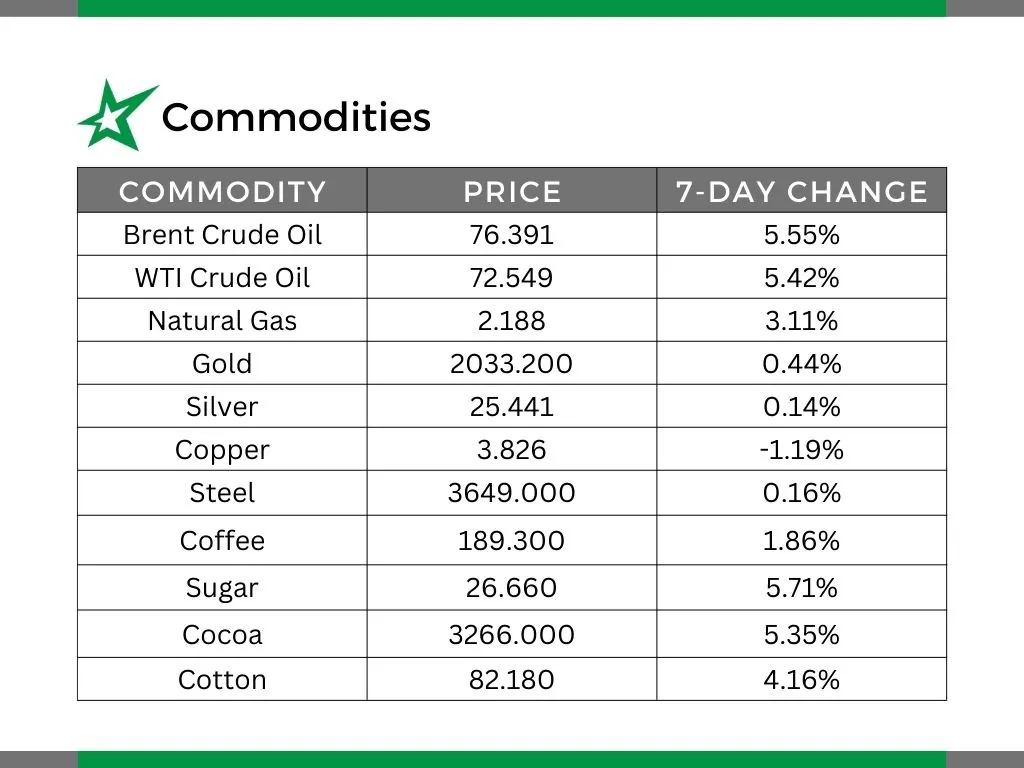
Commodities
-
Concept of the Week: Risk versus Speculation
-
Quote of the Week
Market Moving Headlines
-
The annual inflation rate in the US edged lower to 4.9% in April 2023.
-
US economic optimism index falls to lowest level since November 2022.
-
Mortgage applications in the US jumped 6.3% the first week of May 2023.
-
Copper drops to 4-month low.
-
US crude inventories have biggest weekly increase in 11 weeks.
-
British Pound hits 12-month high.
-
Canada building permits soar by 11.3% from a month earlier.
-
Uranium hovers close to a 1-year high.
-
Japan index of leading economic indicators falls in March 2023.
-
Mexico’s inflation rate drops to a 1-1/2-year low.
-
Sugar approaches an 11-year high.
-
The NFIB small business optimism index in the US fell to its lowest level since 2013.
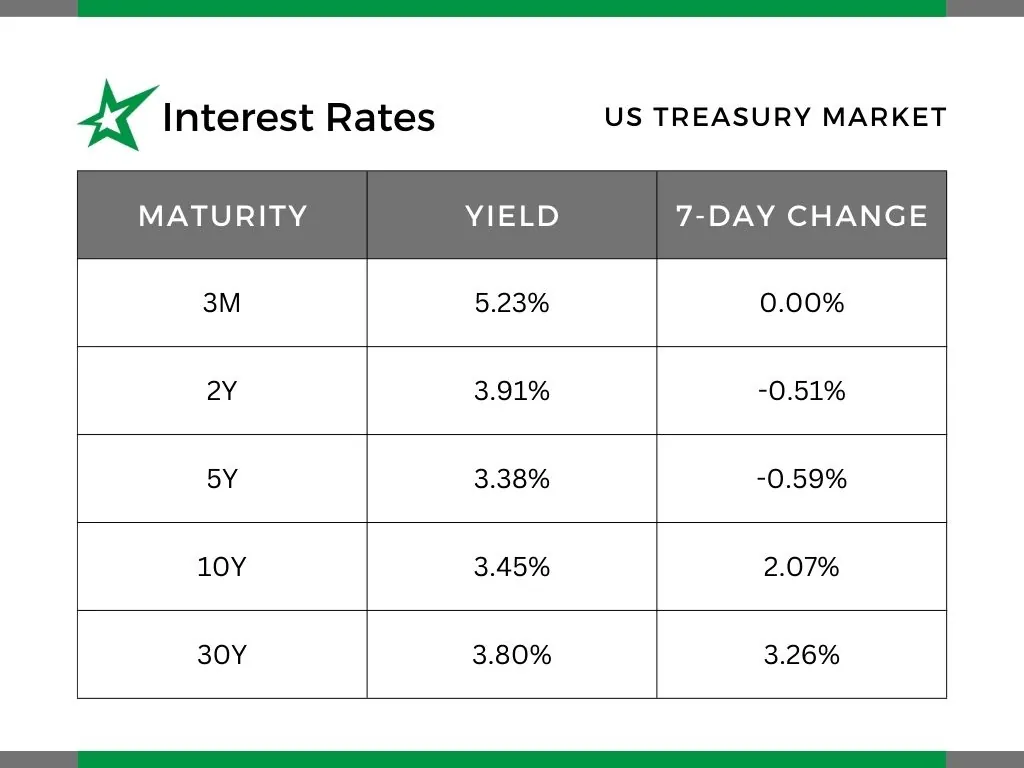
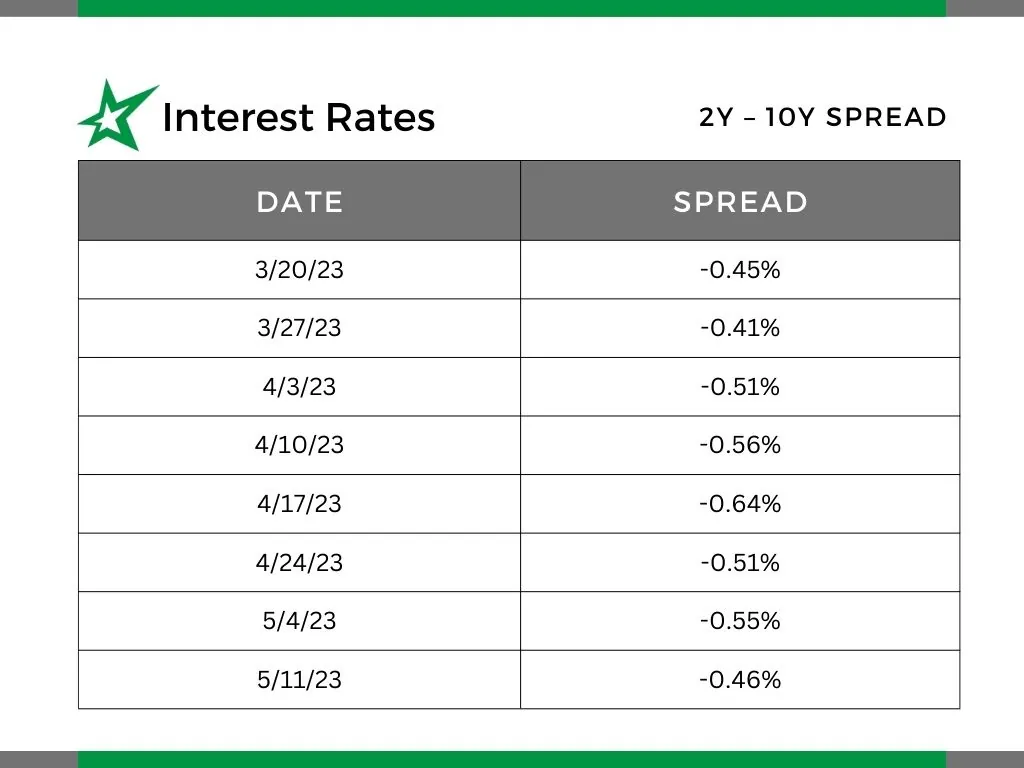
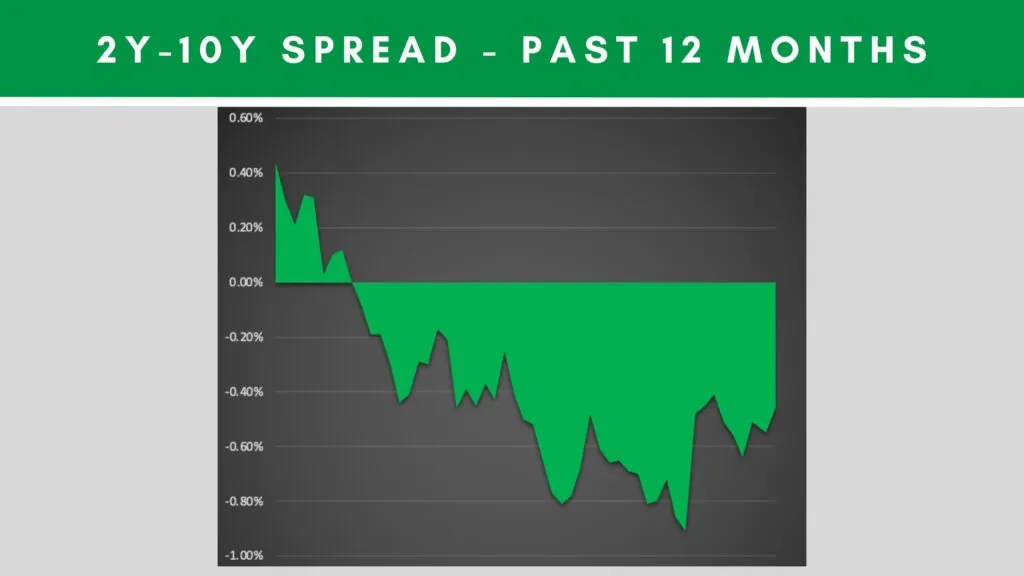
Interest Rates
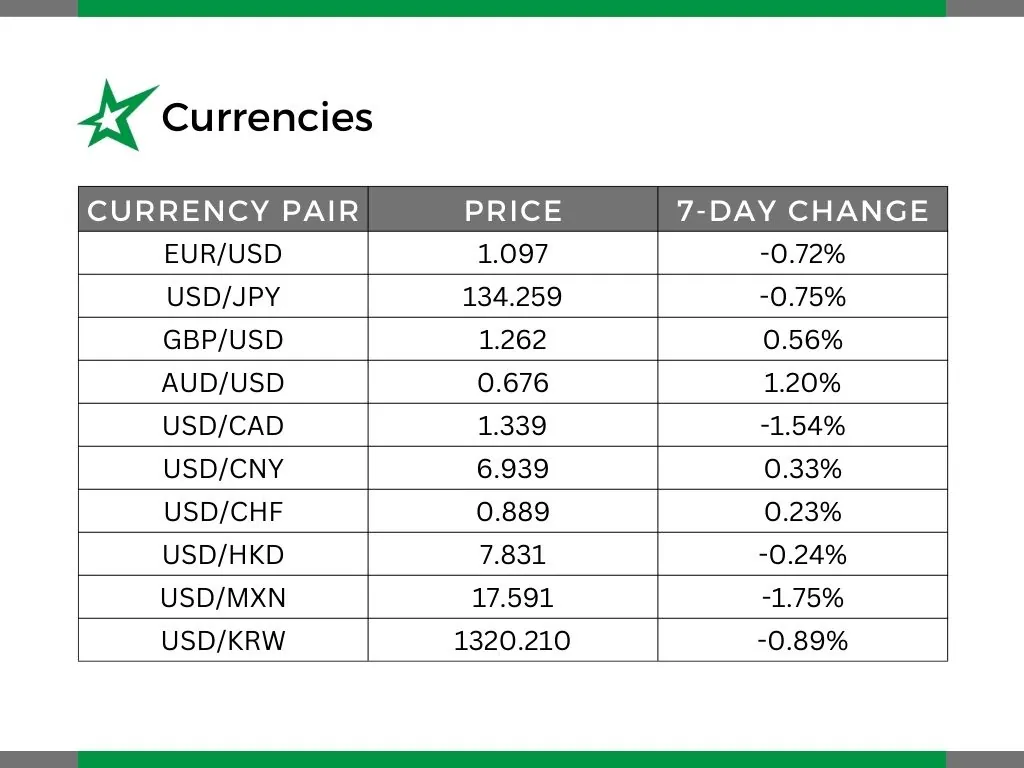
Currencies
Concept of the Week: Interest Rate Swaps
Interest rate swaps provide a means to manage and mitigate interest rate risk. They allow organizations to convert fixed-rate debt into floating-rate debt or vice versa, providing flexibility in managing their exposure to interest rate fluctuations. As with any financial instrument, there are advantages and disadvantages to using interest rate swaps.
Advantages include:
-
Customization: Interest rate swaps can be tailored to meet specific hedging needs. Parties can agree on various terms allowing for customization to match the company’s risk profile.
-
Cost Efficiency: Interest rate swaps can be a cost-effective way to hedge interest rate risk compared to other financial instruments and strategies. Instead or restructuring existing debt or entering into new borrowing arrangements, swaps all organizations to modify their risk exposure without incurring significant transaction costs.
-
Liquidity: Interest rate swaps are highly liquid, allowing for greater price transparency and ease of termination.
-
Accounting Friendly: Interest rate swaps are hedge accounting friendly, which keeps the periodic changes in the swaps’ value from adversely impacting earnings.
Disadvantages include:
-
Counterparty Credit Risk: The majority of interest rate swaps are over-the-counter (OTC) instruments which have an element of counterparty credit risk. This risk can be minimized or eliminated through collateral requirements.
-
Legal Documentation: There is legal documentation required to enter into an interest rate swap that may require involving outside counsel or an advisor to help with the review and negotiation of the swap agreements.
-
Basis Risk: Basis risk arises when the interest rate swap does not perfectly align with the underlying exposure being hedged. Mismatches in benchmark rates or tenors can result in imperfect hedging, reducing the effectiveness of the swap as a risk management tool.
Most find that the advantages of interest rate swaps outweigh the disadvantages, making them the most popular hedging instrument in the market. In fact, at the time of this writing, interest rate swaps globally have exceeded $414 trillion in notional outstanding according to the Bank of International Settlements – a figure four times the size of all foreign currency exchange contracts.
Quote of the Week
“It’s not about avoiding risks, but about understanding and managing them effectively.” – Michael Bloomberg
Want this article in PDF form? Check it out!
Don’t want to miss any updates? Subscribe to our mailing list, by emailing: marketing@hedgestar.com
Author: John Trefethen, Director and Co-Founder
Mobile: 612-868-6013
Office: 952-746-6040
Email: jtrefethen@hedgestar.com
HedgeStar Media Contact:
Megan Roth, Marketing Manager
Office: 952-746-6056
Email: mroth@hedgestar.com
Check out our services: